Exploring the Film Coating Process for Tablets
Have you ever noticed how some tablets have a shiny, smooth exterior? That's because of a process called tablet coating! Tablet coating is an essential step in the manufacturing of tablets. There are various tablet coating techniques, such as sugar coating, film coating, or enteric coating. Among them, film coating is the most popular method in the pharmaceutical and nutraceutical industries.
Today we'll explore the ins and outs of the film coating process. In this blog post, we will cover the different types of tablet coating, the components of film coating formulations, the steps involved, and the benefits of this method, as well as the defects that may occur during film coating. So, if you're curious about the magic behind the shiny exterior of your tablets, keep reading!
What is Film Coating?
Film coating is like putting a nice jacket on your pill. It's a process where a thin layer of polymer is applied to the surface of tablets to make them look shiny, colorful, and more attractive to the eye.
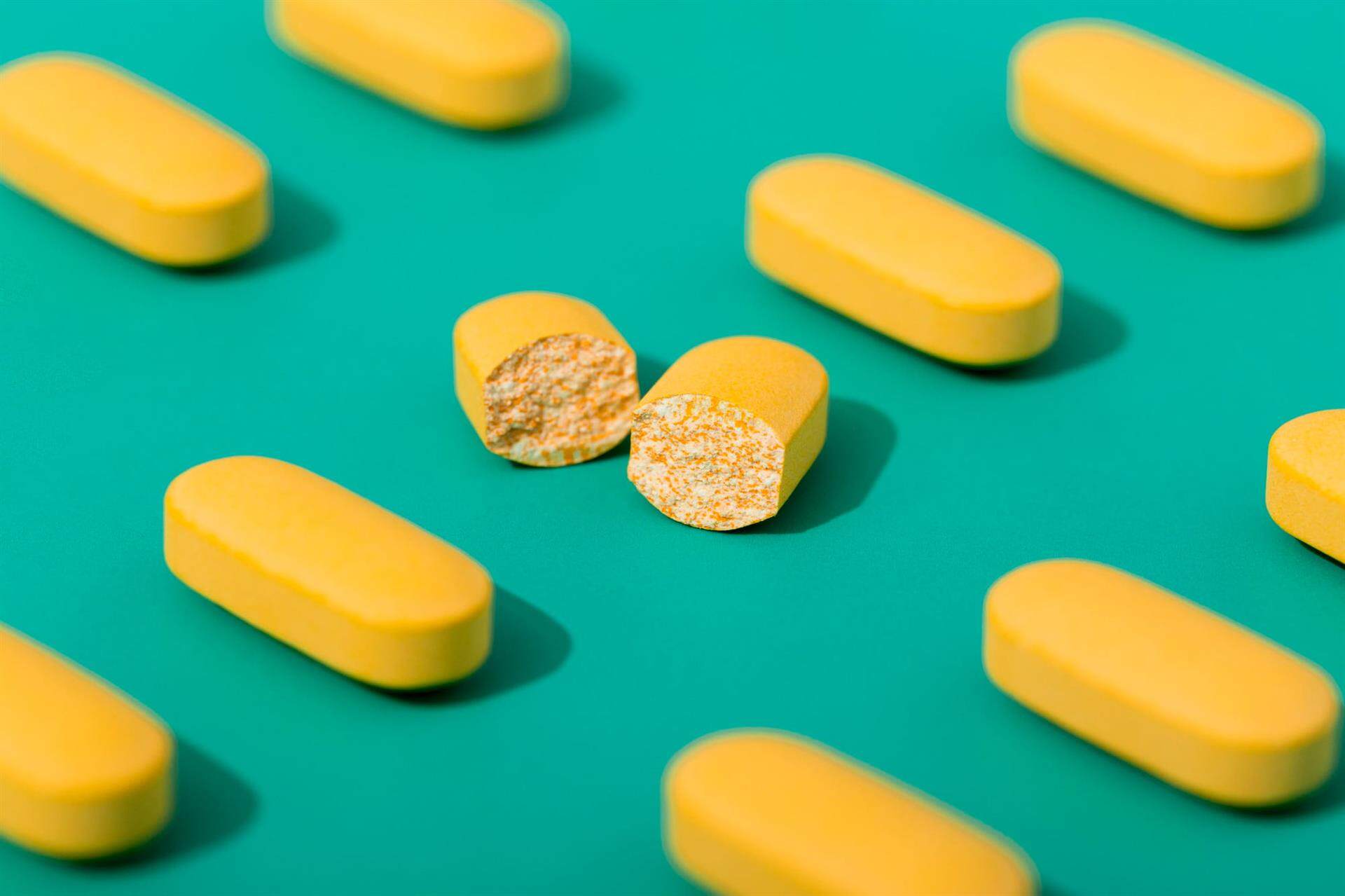

Yet, film coating isn't just about the look. It also serves other important purposes. This process protects the tablet's active ingredients from exposure to air, moisture, and light. This helps to maintain the stability and efficacy of your medication, maximizing the therapeutic potential.
Additionally, the film coating process can mask unpleasant tastes and odors that may be associated with certain drugs. It can also make the tablet easier to swallow, especially for those who have difficulty swallowing larger pills.
Read more:
Enteric-Coated VS Film-Coated Tablets: What's The Difference?
Film Coating VS Sugar Coating: A Complete Guide
The Ultimate Guide To Buying A Film Coating Machines
Different Types of Film Coating
There are many different ways to classify film coating:
|
Factors |
Types |
|
Function |
Enteric Coating: Protects the active ingredient of a tablet from the stomach's acidic environment and releases it in the intestines. |
|
Sustained-release Coating: Releases the active ingredient slowly over time. |
|
|
Taste-masking Coating: Improves the taste and odor of the tablets. |
|
|
Solvent System |
Aqueous Coating: Water-soluble, environmentally friendly, and biocompatible. Releases the drug quickly. |
|
Non-aqueous Coating: Preferred for drugs that are incompatible with water or have poor solubility in water. Provides an enteric coating. Less environmentally friendly. |
|
|
Method of Application |
Pan Coating: Suitable for large batches of tablets. Precisely controls the coating thickness. |
|
Spray Coating: Fast and efficient. Can be used for large surface areas. Offers excellent coverage and uniformity. |
|
|
Dip Coating: Suitable for small batches of tablets. Can be used to coat complex shapes. |
How Does the Film Coating Process Work?
While the concept of filling coating may seem straightforward, the actual process can be quite complex. It requires specialized equipment and expertise to perform effectively. Here's a step-by-step breakdown of how the film coating process typically works:
STEP 1: Preparing the Coating Formulations
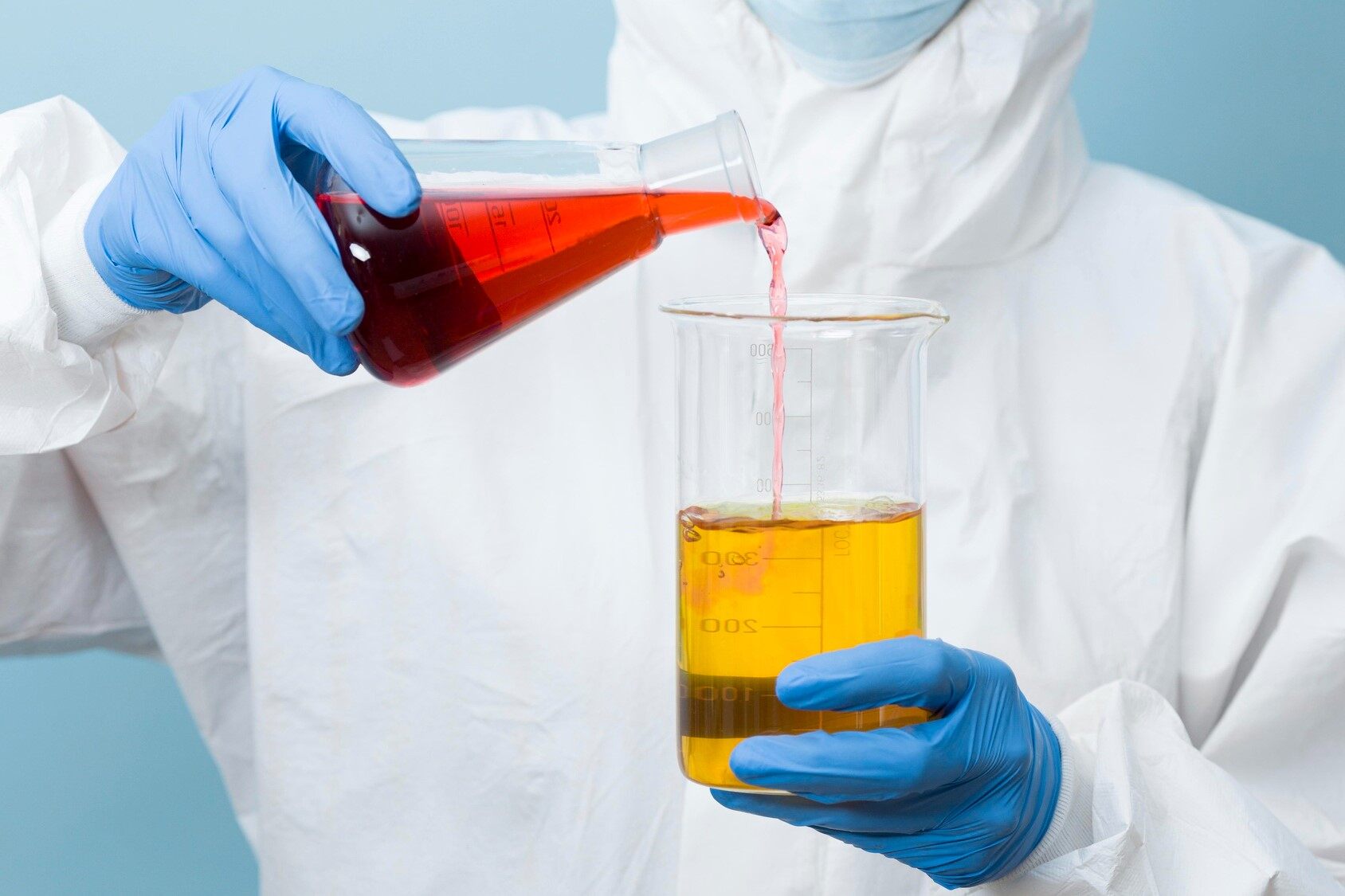

The first step in the film coating process is to prepare the coating solution. The solution is generally formulated with polymers, plasticizers, colorants, solvents, etc. These components are mixed together in appropriate proportions to create a uniform film coating formulation.
Major components of the filling coating formulations:
|
Components |
Functions |
|
Polymers |
|
|
Plasticizers |
|
|
Colorants |
|
|
Solvents |
|
STEP 2: Loading the Tablets
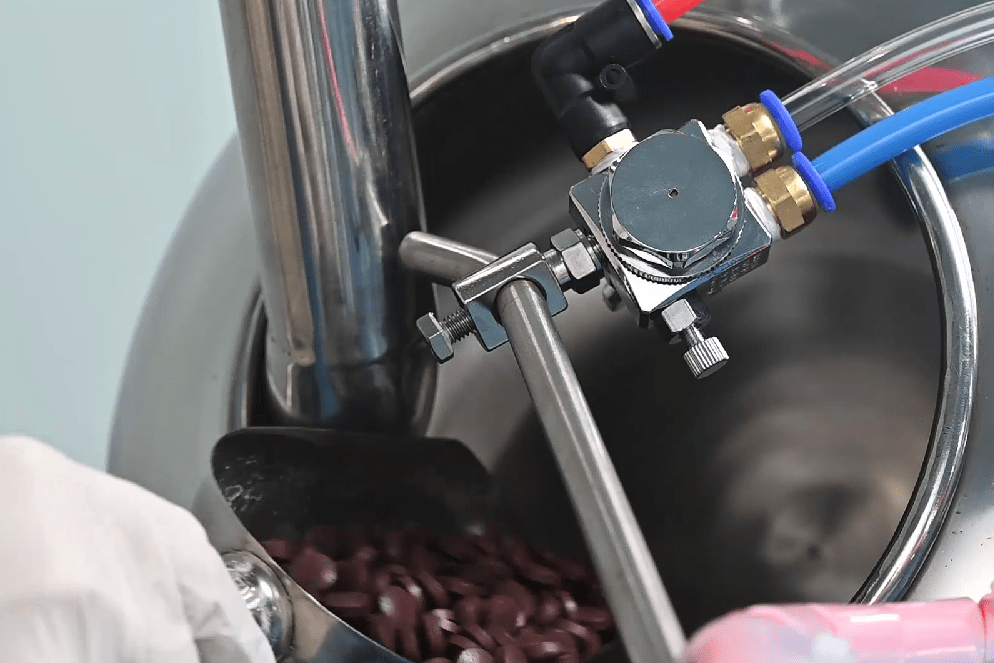
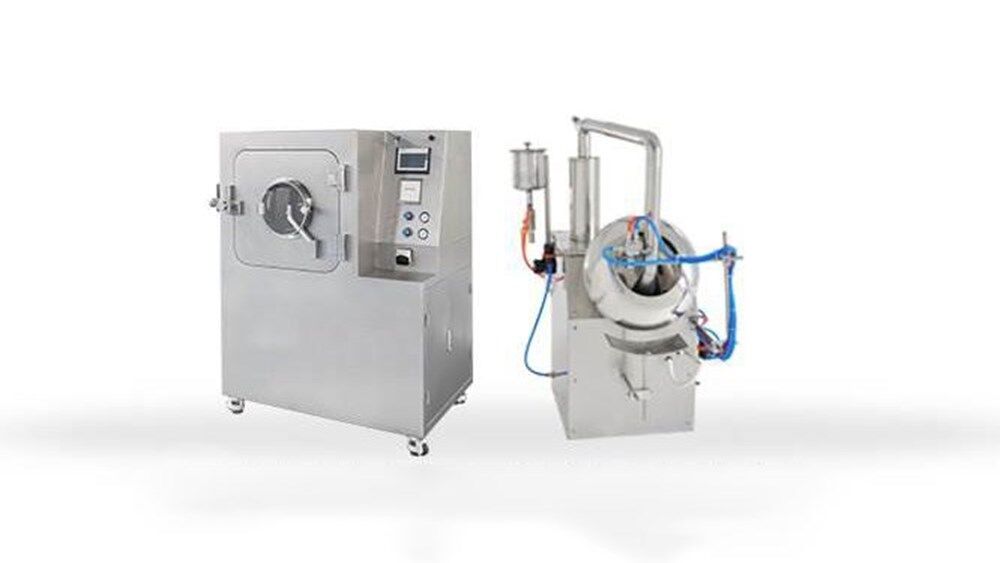
The next step is to load the tablets into the coating machine. This is typically done manually or using a hopper or feeder that feeds the dosage form into the coating pan. The coating pan is a rotating drum that tumbles the tablets as the coating solution is sprayed onto them.
STEP 3: Applying the Coating Solution
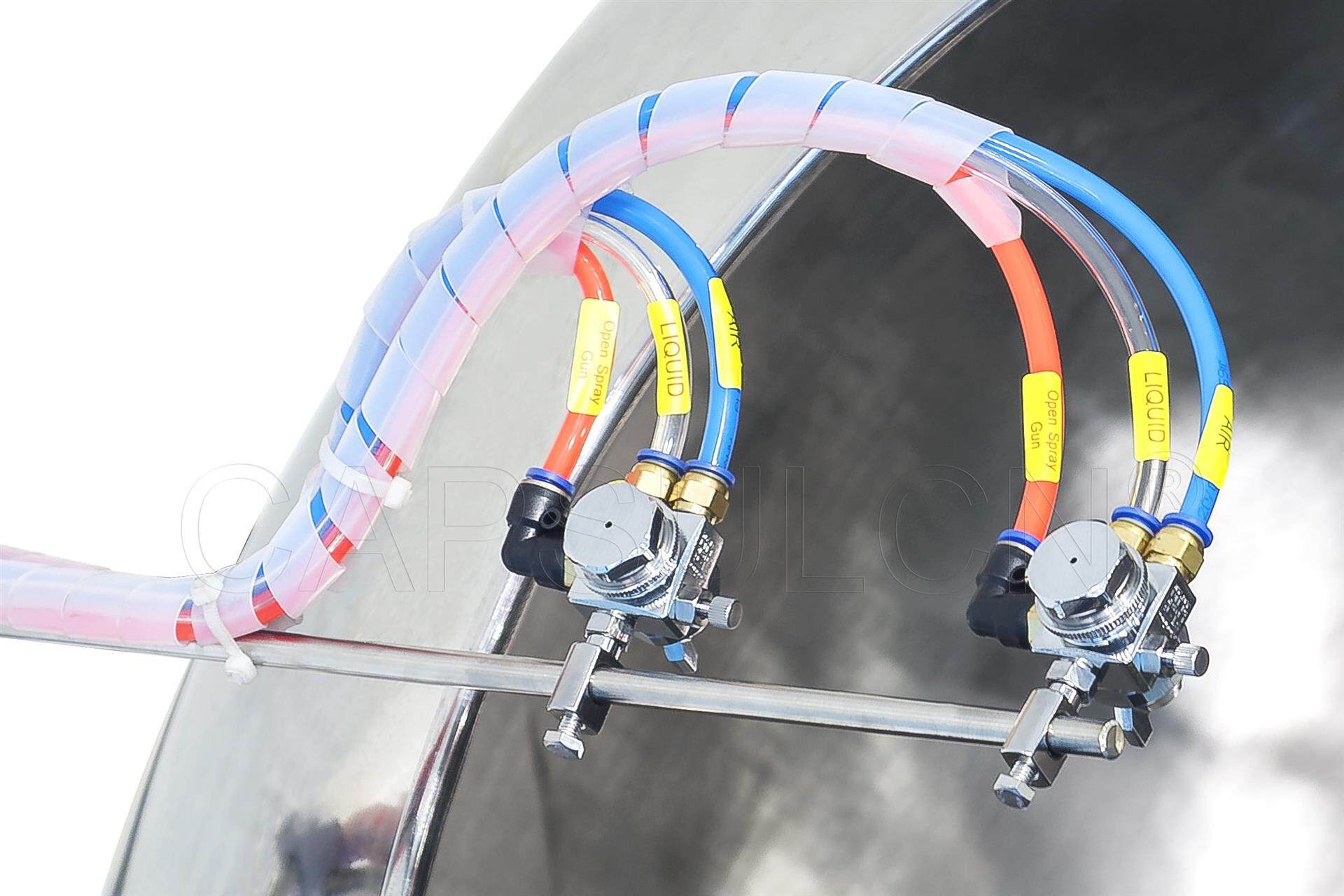

Once the tablets are loaded into the coating pan, the coating solution is sprayed onto them using a spray nozzle. The spray nozzle is positioned above the dosage form. As the coating pan rotates, the nozzle sprays the coating solution onto the tablets.
The spray rate, nozzle position, and other parameters are carefully controlled to ensure that the coating solution is evenly distributed over the surface of the tablets. The spray nozzle may move back and forth or up and down to ensure the batch is fully coated.
STEP 4: Drying the Coating
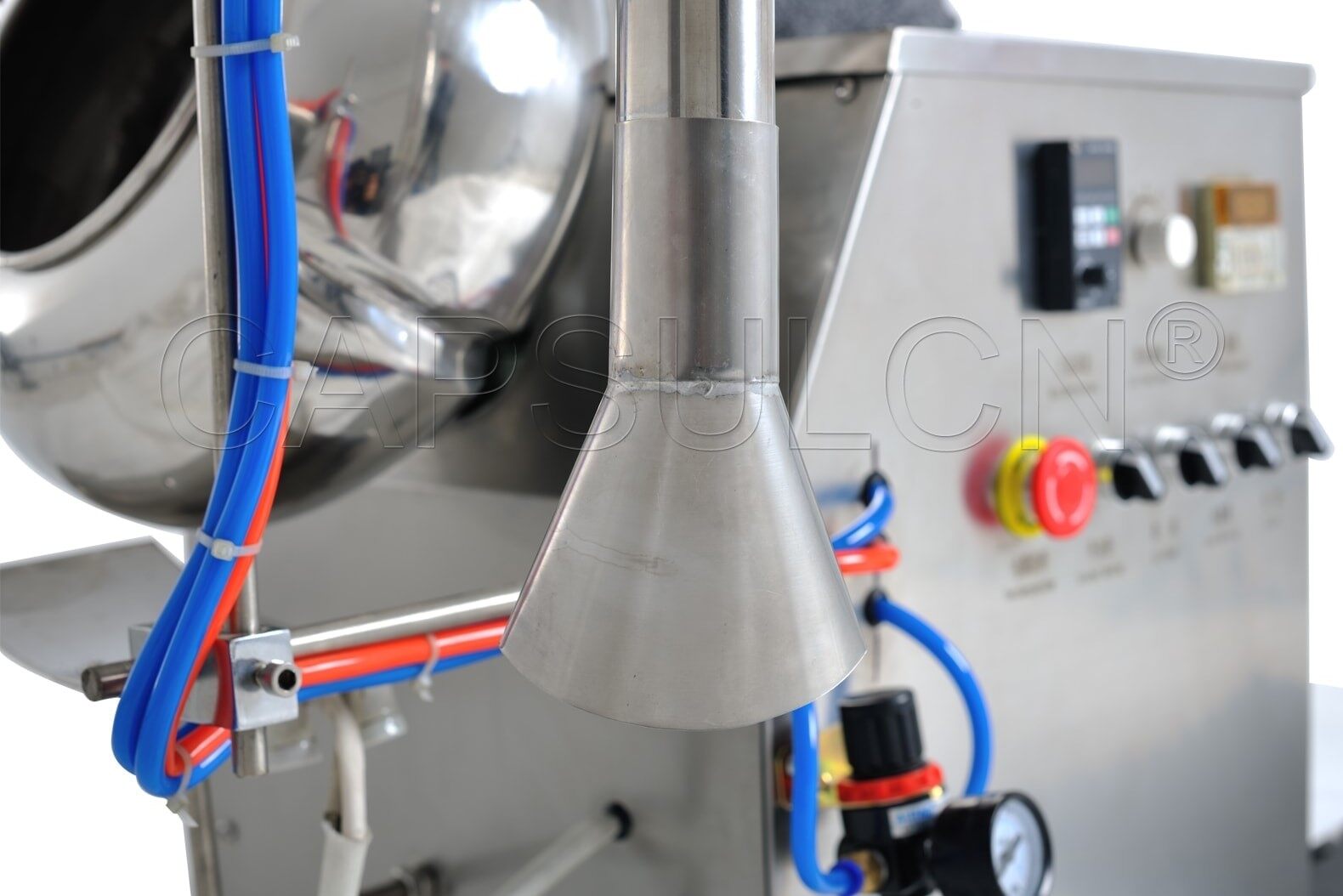

As the coating solution is sprayed onto the tablets, it quickly dries to form a thin, uniform film. The drying process is typically accomplished using heated air. The air is blown over the tablets as they tumble in the coating pan.
The temperature and airflow rate are carefully controlled to ensure the coating dries quickly and evenly. The drying time may change based on the coating type and the film's thickness.
STEP 5: Inspecting the Film-Coated Tablets
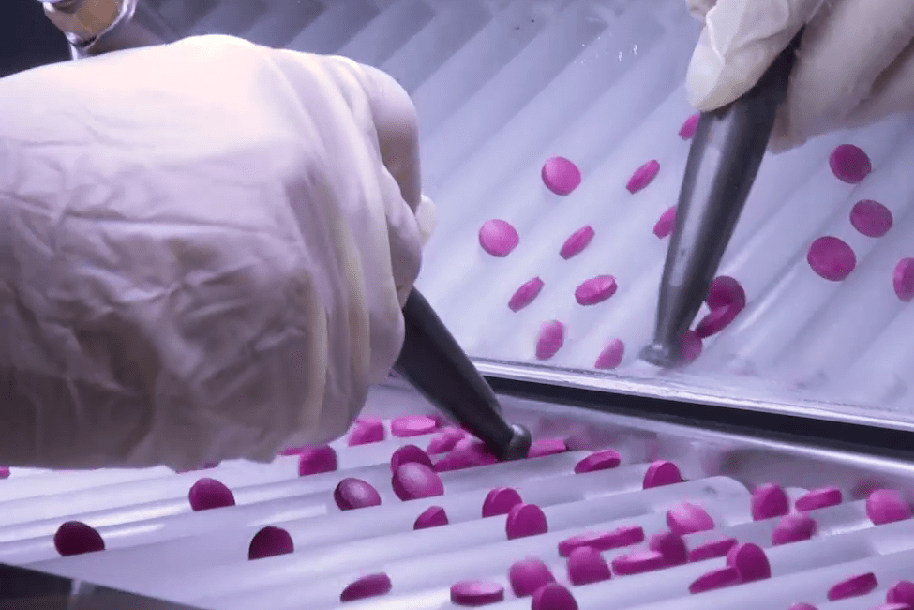

Once the coating is dry, the tablets are inspected to ensure that the coating is uniform and free of defects. This can be done manually or using automated inspection machines. Any defects, such as cracks or uneven coating, may require the dosage form to be recoated or rejected.
Benefits of Film Coating
Film coating offers several benefits in tablet manufacturing. Some of the key benefits include:
Appearance: The film coating can make your tablet visually appealing by adding color or providing a glossy or matte finish to the tablet. This can help to make your medication stand out from other drugs on the market.

Masking: The film coating can mask the unpleasant taste or odor of the tablet, making it more palatable for the patient. This is particularly important for active ingredients with a bitter or unpleasant taste.
Automation: The filling coating is performed by a higher degree of automation. This helps to boost production capacity and efficiency. The coating process can be completed with minimal manual intervention. This reduces the risk of human errors and improves the consistency of the final product. Automation also helps to reduce labor costs and save time.

Protection: The film coating can protect the tablet from moisture, light, and other environmental factors affecting its stability and efficacy. This can help improve the tablet's stability for longer shelf life.
Controlled Release: The film coating can be used to control the release of the tablet over time. This can be particularly important for drugs that need to be released slowly over a period of time to maintain therapeutic levels in the desired location of the gastrointestinal tract.
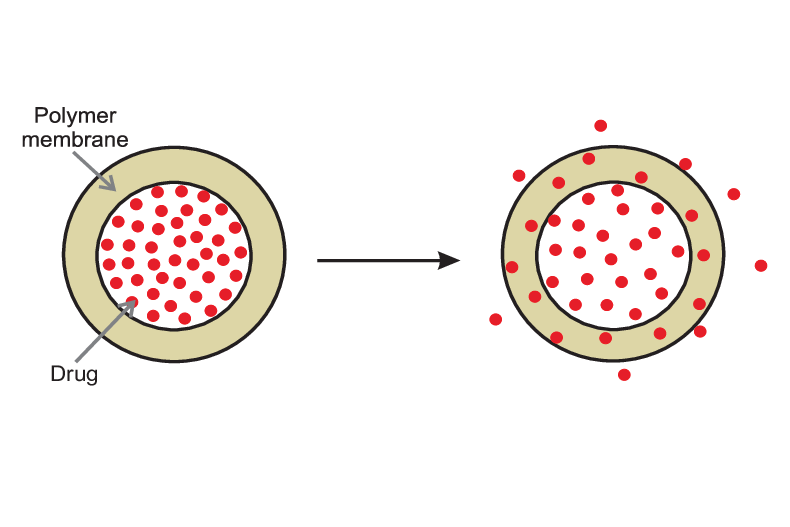
Cost-effectiveness: Compared to sugar coating, the film coating process is more economical. It can produce tablets that are less bulky, more attractive, and easier to swallow, improving patient compliance.
Visual Defects During Film Coating Process and Their Remedies
There are several defects may occur during tablet film coating. In this section, we will highlight some common defects and how you can troubleshoot them.
Mottling:
- Uneven distribution of color or pigment on the tablet surface, resulting in a mottled or spotty appearance.
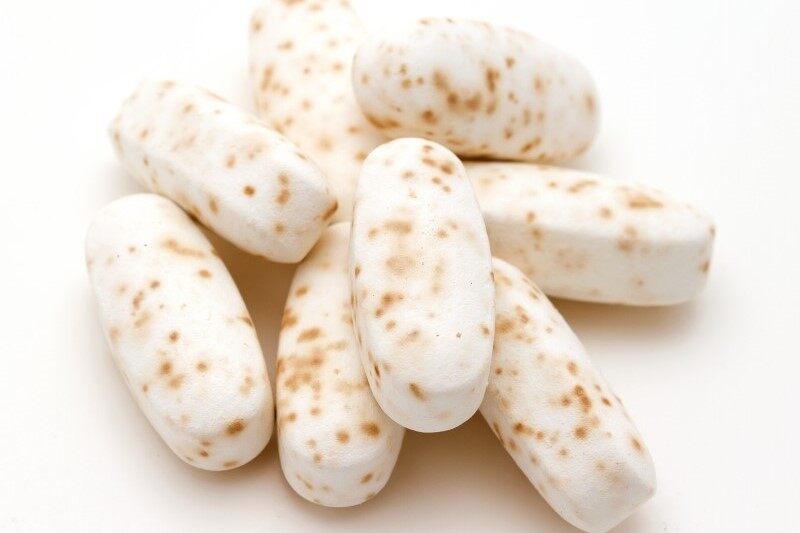

Remedies:
- Use appropriate colorants
- Change the solvent system
- Mix the coating solution properly
- Adjust spray rate and drying temperature
- Increase the coating pan speed
Orange Peel:
- The tablet surface appears rough or uneven, similar to the texture of an orange peel.
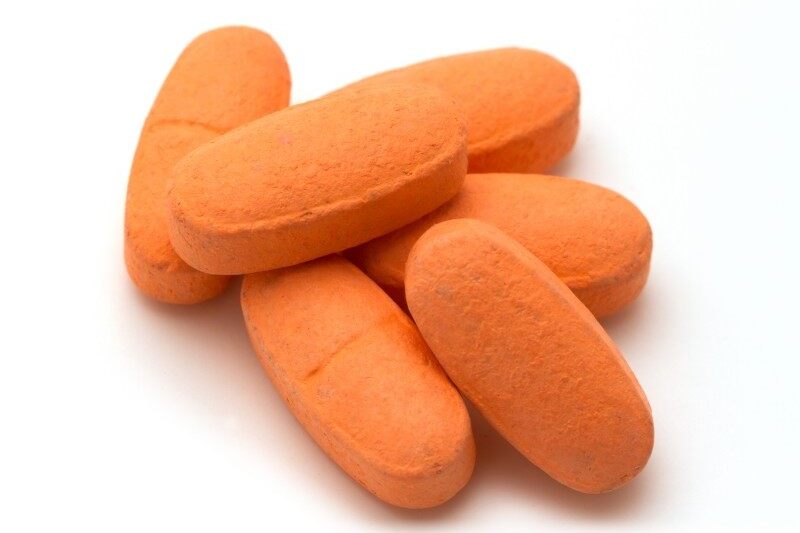

Remedies:
- Decrease the viscosity of the coating formulation
- Optimize the atomizing air pressure
- Balance the drying conditions and spray rates.
Bridging:
- Coating material bridges across the tablet edges, causing them to stick together.
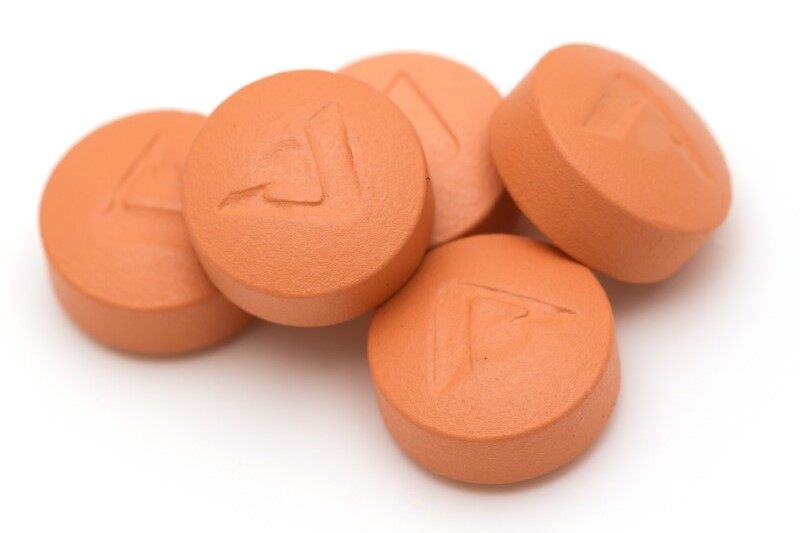

Remedies:
- Increase temperature
- Decrease spray rate
- Optimize the atomizing air pressure
- Change the plasticizer
Cracking:
- The coating on the tablet surface develops cracks or splits, exposing the tablet core.
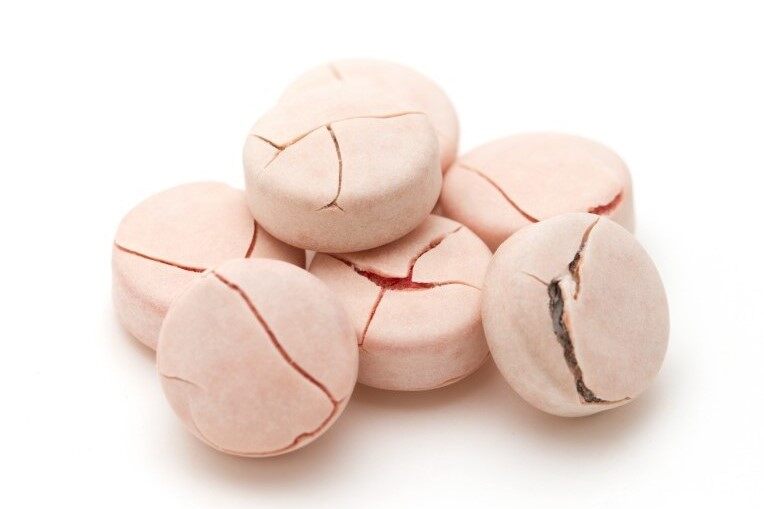

Remedies:
- Adjust processing temperature and spray rate
- Use lower molecular weight polymers
- Adjust plasticizer type and concentration
Blistering:
- The coating separates from the tablet surface, forming blisters or bubbles.

Remedies:
- Use mild drying conditions
Peeling:
- The coating peels off the tablet surface, leaving patches of uncoated areas.
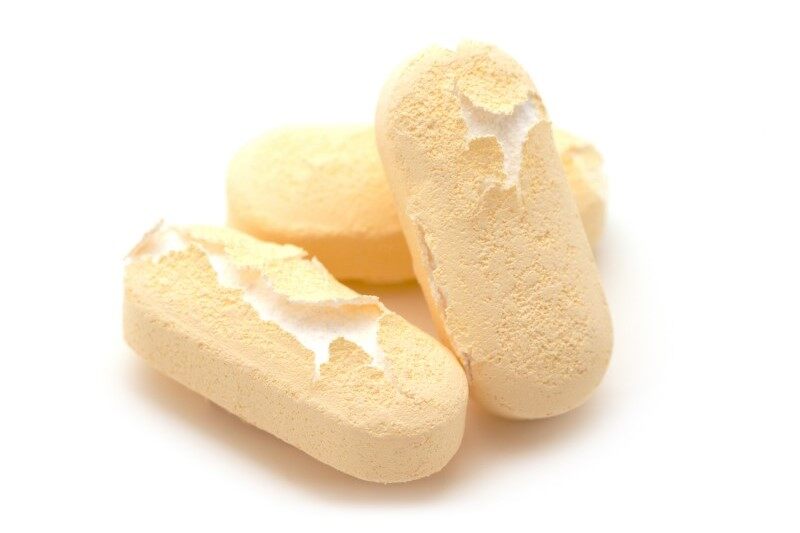

Remedies:
- Reduce air temperature
- Increase spray rate
- Reduce the coating pan speed
Picking:
- The coating sticks to the machine and is pulled off the tablet surface, causing small holes or craters.

Remedies:
- Reduce spray rate
- Increase drying temperature
- Increase the coating pan speed
- Increase the atomizing air pressure
- Optimize the spray gun setup
Film Coating Solutions at iPharMachine
Are you looking for top-notch solutions for film coating? Look no further than iPharMachine! We specialize in providing high-quality tablet coaters and support services to help streamline your tablet manufacturing process. Contact us today to learn more about tablet coating!
Leave your comment
Also Offers


Containment Automatic Capsule Filling Machine SFK-703

Fully Automatic Dosator Capsule Filling Machine CZ-40

Our Team
As an expert in the pharmaceutical and pharmaceutical packaging industry, iPharMachine has provided solutions for hundreds of pharmaceutical and health product manufacturers for 17 years. By visiting customers, we get good reviews from our customers.
- info@ipharmachine.com
- English Español Deutsche







